Zinc pyrithione(ZPT)
Zinc pyrithione(ZPT)
Factory supply Zinc pyrithione(ZPT) 13463-41-7 with sufficient production capacity
- Molecular Formula:2(C5H4NOS).Zn
- Molecular Weight:317.708
- Appearance/Colour:Fine beige granules
- Vapor Pressure:0.00275mmHg at 25°C
- Melting Point:262oC
- Boiling Point:253.8 °C at 760 mmHg
- Flash Point:107.3 °C
- PSA:101.52000
- Density:1.782 g/cm3 (25oC)
- LogP:3.34050
Zinc pyrithione(Cas 13463-41-7) Usage
|
Product description |
Zinc pyrithione is the pyrithione complexes of zinc bromide, in the early 1930s, was already synthesized and used as a topical antifungal or antibacterial agent. At room temperature it is white to yellow crystalline powder. Slight characteristic odor. Insoluble in water. Solubility: water 15mg/kg; pH = 8 Water 35mg/kg; Ethanol 100mg/kg; polyethylene glycol (PEG400) 2000mg/kg. A pH optimum range of 4.5 to 9.5; mass fraction of 10% suspension pH3.6. Zinc pyrithione react with cationic and non-ionic surfactants forming insoluble precipitate, unstable in the light and oxidizer, when at higher temperatures ,it is not stable to acids and bases . It is not compatible with EDTA, non-ionic surfactants make it partially deactivated. When with the presence of heavy metals, chelation or anti-sequestration will occur, and these chelates are insoluble in water. EEC and GB7916-87 provide that maximum allowable concentration of mass fraction of zinc pyrithione on cosmetics is 0.5%, only for cleaning after using products.General concentration 250~1000mg/kg (active), zinc pyrithione can be used in gels, creams, lotions, talcum powder and anti-dandruff shampoo, deodorant and also for disinfecting articles. |
|
Pharmaceutical Applications |
Zinc pyrithione is a regulator of keratinization, selenium sulfide has antimicrobial properties and ketoconazole is an antifungal agent (i.e.can provide the reduction of the lipophilic yeast Malassezia furfur). |
|
Efficacy |
Zinc pyrithione shampoos (in concentrations between 1 to 2%) and shampoos with selenium sulide have been reported to be effective in the treatment of scalp psoriasis.However,their efficacy has not been substantiated by controlled studies.There is also some evidence that shampoos with antifungal agents (e.g.ketoconazole)can have a beneficial effect on scalp conditions. It should be noted, however, that the effectiveness of these shampoos is much smaller than these containing tars, corticosteroids or keratolytics. |
|
Photolysis |
Zinc pyrithione is very rapidly transformed by photolysis. Experiments conducted under sterile conditions with a light:dark cycle of 12:12 hours have shown that, under exposure to light, the concentration of [pyridine-2,6-14C]zinc pyrithione in pH 9 buffer was reduced to 33% of the radioactivity added in 15 min. Data from this study also demonstrated that less than 5% of the 14C added occurred as zinc pyrithione after 1 hour of exposure to light. Similar results have been achieved when photolysis of zinc pyrithione was investigated by use of artificial seawater. In this study, the parent compound constituted 45% of the radioactivity added after 15 min while, after 24 hours, 1.3% of the added dose occurred as zinc pyrithione. The estimated half-lives of the photolytic transformation of zinc pyrithione was 13 min in pH 9 buffer and 17.5 min in artificial seawater (Reynolds 1995a). https://www2.mst.dk/udgiv/publications/2000/87-7944-084-3/html/kap04_eng.htm |
|
Toxicity evaluation |
The toxicity of the active substance zinc pyrithione has been investigated in standard laboratory tests with a number of aquatic organisms living in fresh water (the green alga Selenastrum capricornutum, the crustacean Daphnia magna, the fish rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas)) and in seawater (the crustacean Mysidopsis bahia, the fish sheepshead minnow (Cyprinodon variegatus) and the oyster (Crassostrea virginica)) (Boeri et al. 1993; 1994a-e; Ward et al. 1994a). The results show that while zinc pyrithione and omadine disulfide were very toxic to aquatic organisms (L(E)C50 in the order of 3-300 μg/L), omadine sulfonic acid and pyridine sulfonic acid were considerably less toxic (L(E)C50 in the order of >20 mg/L) (Olin 1977). In a long-term study with fish eggs and larvae, pyridine sulfonic acid gave no effects at a concentration of 0.01 mg/L (Boeri et al. 1999). Algae were the group of organisms most sensitive to the last two substances. |
|
Indications |
Zinc pyrithione is the active ingredient in several shampoos used to control dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis and is also effective in the therapy of tinea versicolor. It remains unclear whether the beneficial effects are caused by an antiproliferative or antimicrobial effect or both. It is substantive to the hair, allowing continued therapeutic effect after washing. |
|
Brand name |
Head & Shoulders Conditioner (Procter & Gamble). |
|
General Description |
Fine beige granules. |
|
Air & Water Reactions |
Insoluble in water. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
Organometallics, such as Zinc pyrithione, are reactive with many other groups. Incompatible with acids and bases. Organometallics are good reducing agents and therefore incompatible with oxidizing agents. Often reactive with water to generate toxic or flammable gases. |
|
Fire Hazard |
Flash point data for Zinc pyrithione are not available, but Zinc pyrithione is probably combustible. |
|
Contact allergens |
Zinc pyrithione is widely used in antidandruff shampoos and is a classic allergen. Concomitant reactions are expected to both zinc and sodium pyrithione. |
|
Safety Profile |
Poison by ingestion, skin contact, intraperitoneal, and intravenous routes. Moderately toxic by subcutaneous route. An experimental teratogen. Experimental reproductive effects. An eye irritant. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NOx, SOx, and ZnO. Used as an anti- dandruff agent in shampoos. See also ZINC COMPOUNDS and SULFIDES. |
InChI:InChI=1/2C5H4NOS.Zn/c2*7-6-4-2-1-3-5(6)8;/h2*1-4H;/q2*-1;+2
13463-41-7 Relevant articles
Novel synthesis of Bis (N-oxopyridine-2-thionato) zinc (II) using solid precursors
Jo, Won-young,Paek, Seung-Min,Park, Man,Hwang, Seong-Ju,Choy, Jin-Ho
, p. 1071 - 1074 (2006)
Unprecedented solid-transchelation react...
Synthesis of Bis(trityl)iron(II) and Formation of the Iron(0)-Stabilized o, o-Isomer of Gomberg's Dimer
Hayton, Trevor W.,Touchton, Alexander J.,Wu, Guang
supporting information, p. 4045 - 4049 (2021/12/13)
Treatment of Fe(OAc)2 in THF with 2 equi...
Protonation and electrochemical properties of a bisphosphide diiron hexacarbonyl complex bearing amino groups on the phosphide bridge
Shimamura, Takehiko,Maeno, Yuki,Kubo, Kazuyuki,Kume, Shoko,Greco, Claudio,Mizuta, Tsutomu
, p. 16595 - 16603 (2019/11/19)
A bisphosphide-bridged diiron hexacarbon...
Phosphorus-carbon bond forming reactions of iron tetracarbonyl-coordinated phosphenium ions
King, Ryan C.,Nilewar, Shrikant,Sterenberg, Brian T.
, p. 68 - 74 (2018/11/21)
Abstraction of chloride from [Fe(CO)4(PP...
Iron Catalyzed Hydroformylation of Alkenes under Mild Conditions: Evidence of an Fe(II) Catalyzed Process
Pandey, Swechchha,Raj, K. Vipin,Shinde, Dinesh R.,Vanka, Kumar,Kashyap, Varchaswal,Kurungot, Sreekumar,Vinod,Chikkali, Samir H.
supporting information, p. 4430 - 4439 (2018/04/05)
Earth abundant, first row transition met...
13463-41-7 Process route
-
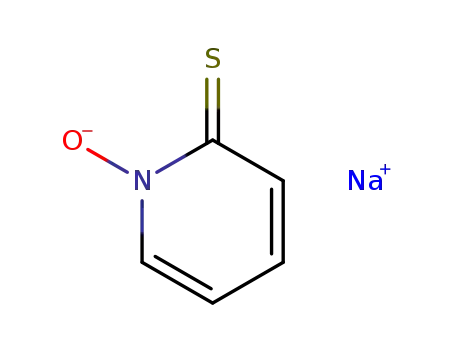
- 3811-73-2
2-mercaptopyridine-1-oxide sodium salt
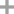
-
- 7646-85-7,24359-56-6
zinc(II) chloride

-
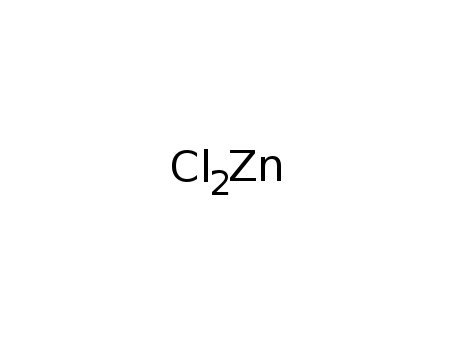
- 13463-41-7
zinc pyrithione
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
In water; at 70 ℃; for 1.16667h; Product distribution / selectivity;
|
99.1% |
-
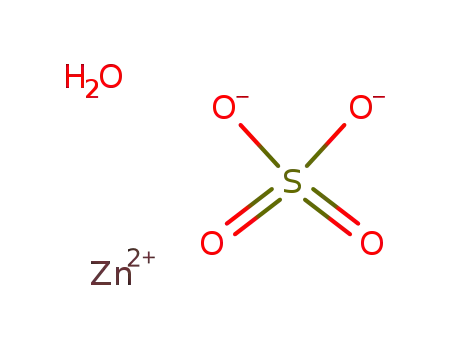
- 100685-55-0
zinc(II) sulfate monohydrate

-

- 3811-73-2
2-mercaptopyridine-1-oxide sodium salt

-

- 13463-41-7
zinc pyrithione
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
In water;
|
|
|
In water;
|
13463-41-7 Upstream products
-
3811-73-2

2-mercaptopyridine-1-oxide sodium salt
-
7646-85-7

zinc(II) chloride
-
100685-55-0

zinc(II) sulfate monohydrate
-
10196-18-6
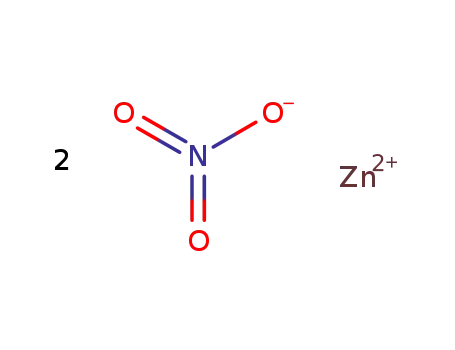
zinc(II) nitrate








 2254784343
2254784343